Energy performance certificates are important documents in the property market and they have to be provided legally when renting or selling a property as part of the prescribed document pack that has to be made available to the buyer or renter. In this guide we will take a look at EPC certificates, how they are calculated and what they actually mean.
What is an Energy Performance Certificate?
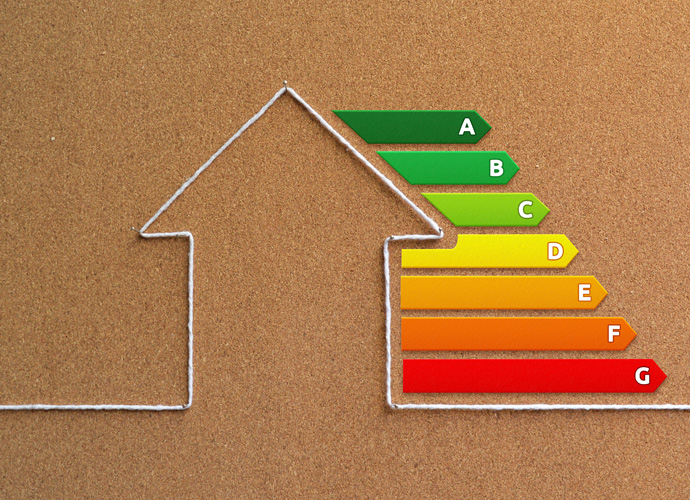
An energy performance certificate is a document with an energy efficiency rating from A-G which gives a quantified assessment of the energy performance of the property. A is the most energy efficient and G is the least energy efficient. The document will also give an indication as to the best possible rating that could be achieved and the improvements, including costs and potential savings, that would be needed to achieve that rating. The certificate will give a rating for each element such as insulation in walls and roof spaces and heating and hot water from Very good to very poor to give the detail as to how good each individual energy efficiency aspect of the property is rated.
What are the EPC bandings?
EPCs are rated from A to G according to the following scoring system:
- EPC rating A = 92-100 SAP points (Green)
- EPC rating B = 81-91 SAP points (Green)
- EPC rating C = 69-80 SAP points (Green)
- EPC rating D = 55-68 SAP points (Yellow)
- EPC rating E = 39-54 SAP points (Amber)
- EPC rating F = 21-38 SAP points (Orange)
- EPC rating G = 1-20 SAP points (Red)
SAP stands for Standard Assessment Procedure which is a 234 page document detailing how to carry out an EPC inspection and how to calculate the score.
Clearly, we are not going to go into the detail of the procedure in this article, but we will touch upon the main things that will be looked at during the inspection:
Lighting
The assessor will look at the lighting in the property and determine how energy efficient the bulbs are. The overall assessment will look at the total number of light fittings and bulbs and how many are energy efficient LED bulbs. Lighting, in general only has a small effect on the overall EPC rating, maybe 1 or two points, but that can make all the difference.
Windows
Windows and doors contribute to some of the largest energy losses in a property and the more energy efficient they are the better. An assessor will be looking for the u values associated with the windows and also the size of the windows. The u value which is the thermal transmittance of the window should be as low as possible and for modern buildings has to be below 1.6 W/m2k but the lower the better.
Heating
The heating element will form one of the major elements of the assessment and the assessor will take note of the size and age of the boiler, the size of the rooms, the number and size of the radiators, thermostatic controls either via the thermostat or thermostatic valves on the radiators and use those to calculate the EPC value for the heating system.
Insulation
The last major part that the assessor will look at is the loft and wall insulation. Typically lofts should have 270mm of insulation and walls should have cavity wall insulation.
What do EPCs really mean?
EPCs are vital in the rental market and unless there is an exemption, rental properties with an EPC rating worse than an E cannot legally be rented out under current legislation and even with EPC ratings better than an E, the property cannot be rented out without an EPC certificate.
As far as the sales market is concerned, a property cannot be sold on the open market without an EPC certificate.
For those looking to rent or buy a property, the EPC certificate will give them useful information around the energy use in the property and the ongoing running costs. This will allow them to make an informed decision about whether to rent or buy the property.





